Grant information
- NIH R21CA252579
06/01/2021 – 05/31/2023
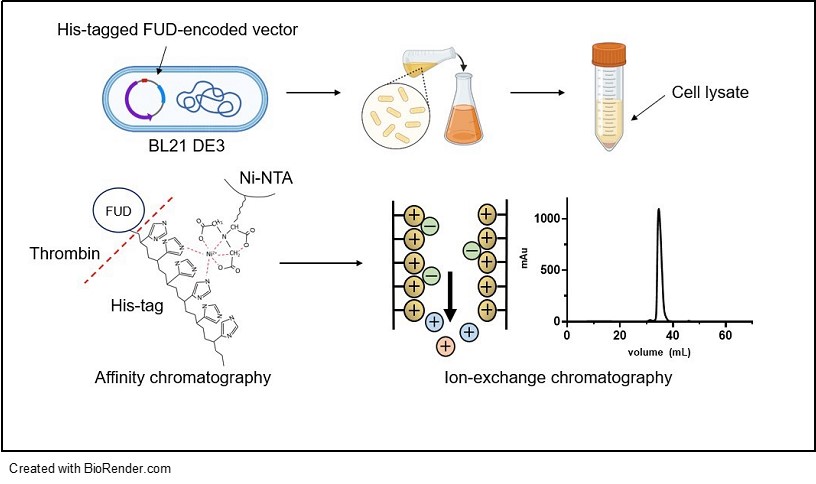
The Kwon Research Group has developed PEG-FUD, a PEGylated peptide inhibitor of fibronectin assembly, by conjugating a 20-kDa PEG to the Functional Upstream Domain (FUD) peptide to enhance pharmaco-kinetics while preserving nanomolar binding affinity for fibronectin’s N-terminal 70-kDa domain critical for fibrillogenesis. Characterization via isothermal titration calorimetry and matrix assembly assays confirmed PEG-FUD retains inhibitory potency comparable to non-PEGylated FUD, with improved plasma stability (>48 hours) and reduced renal clearance. In murine a 4T1 breast model, multimodal imaging revealed PEG-FUD’s enhanced tumor targeting: optical imaging showed prolonged circulation and tumor accumulation after SC injection, while PET/CT with [64Cu]Cu-PEG-FUD demonstrated 2.3-fold higher tumor uptake than unmodified FUD after IV injection (1.35% IA/g vs 0.59% IA/g at 48 hours). PEG-FUD’s ability to disrupt fibronectin-rich TME suggests therapeutic potential by inhibiting ECM remodeling that supports metastasis. Future directions include optimizing dosing regimens for combination therapies with chemotherapeutics, expanding into other fibrotic cancers, and advancing clinical translation as a theranostic agent for simultaneous imaging and targeted treatment of breast cancer.