Grant information
- DoD W81XWH2210693
07/01/2022 – 06/30/2026
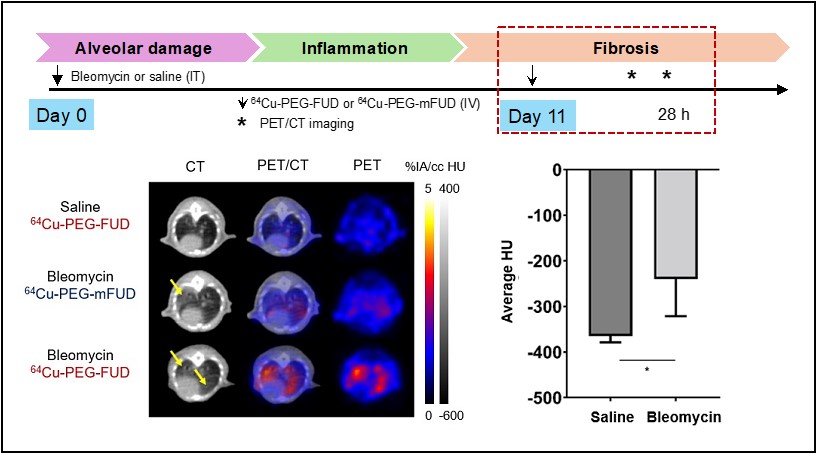
Research on PEG-FUD peptide centers on its development as a potent inhibitor of fibronectin assembly for imaging and treatment of kidney and lung fibrosis. By conjugating the FUD peptide to polyethylene glycol (PEG) of varying sizes (10, 20, and 40 kDa), his team achieved constructs with high purity and retained nanomolar binding affinity to fibronectin, crucial for blocking the formation of fibronectin fibrils that precede collagen deposition and scar tissue formation. In preclinical models, PEG-FUD effectively inhibited fibronectin fibrillogenesis and reduced fibronectin and collagen accumulation in fibrotic kidneys, demonstrating therapeutic potential in the unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) model. For lung fibrosis, PEG-FUD preferentially localized to fibroblastic foci in both human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) lung tissue and murine bleomycin-induced lung injury, supporting its use as a targeted imaging probe for early fibrotic changes and as a candidate for anti-fibrotic therapy. Future perspectives include advancing PEG-FUD as a non-invasive PET imaging agent for early detection of fibrotic disease activity, optimizing dosing for therapeutic efficacy, and expanding clinical translation for both kidney and lung fibrosis.